Introduction
The core components of cells are the outer membrane, the cytoplasm (substance inside which contains all other stuff) and the nucleus (contains DNA). All the other stuff is made up of various components with specific functions – these are called organelles.
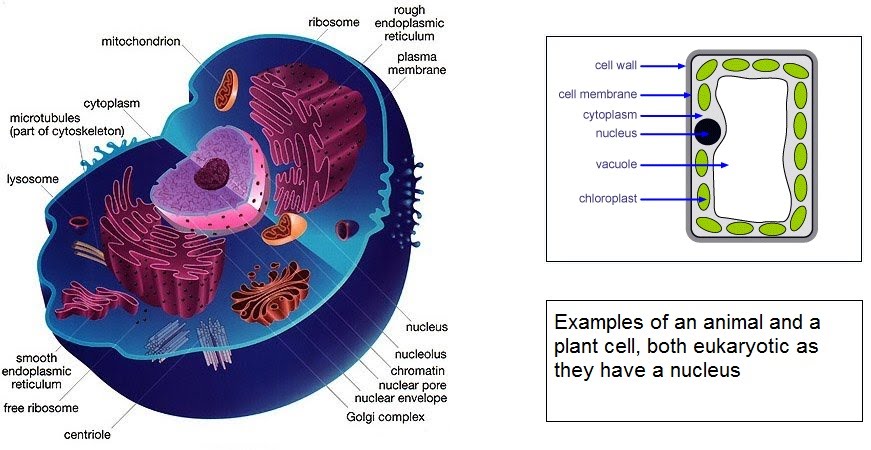
The ones you must know about are:
Centriole
Nucleus
Mitochondria
Chloroplasts (plants and algae)
Golgi apparatus and Golgi vesicles
Lysosomes
Ribosomes
Rough endoplasmic reticulum and smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Cell wall and plasmodesmata (plants, algae, fungi)
Cell vacuole (plants)
In complex multicellular organisms, eukaryotic cells are specialised and therefore organised accordingly into tissues, organs and systems. For example, a small intestine epithelial cell which absorbs nutrients from food is part of the epithelium tissue of the small intestine organ of the digestive system.
So, what are we waiting for? Let’s delve right into these organelles.
Centriole
The centriole is a tubey spaghetti thing that aids in cell division when the duplicated chromosomes need to move into their subsequent new offspring cells from the parent cell (during mitosis)….