Prokaryotic cells
Viruses
Prokaryotic cells
Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus like eukaryotes do. Their DNA is not membrane-bound, just free in the cytoplasm. The extra features of prokaryotic cells vs. eukaryotic cells you must learn are:
-the cytoplasm overall does not contain membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum
-prokaryotic ribosomes are smaller than their eukaryotic counterparts
-as previously covered, and their primary defining element, they lack a nucleus; instead, their DNA is a single circular molecule freely present in the cytoplasm and not associated with any proteins such as histones in eukaryotes
-they have a cell wall which contains a special glycoprotein called murein (also known as peptidoglycan)
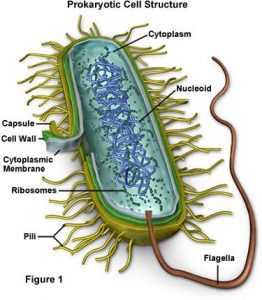
Some prokaryotes also go further to have some specialised parts, some seen in the diagram:
-one or more plasmids which are also circular DNA loops but much smaller; these can be exchanged between cells or even between different species as they can carry genes for antibiotic resistance
-a capsule made of polysaccharides as their outermost layer (on top of the cell wall on top of the plasma membrane)
-one or more flagella which aid in locomotion…
