The nervous system coordinates bodily functions via chemical and electrical signals.
It processes information throughout the body by carrying signals between the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS is composed of the brain and spinal cord, while the PNS consists of nerves which are connected to the CNS and reach the rest of the body.
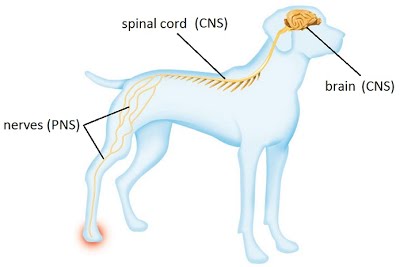
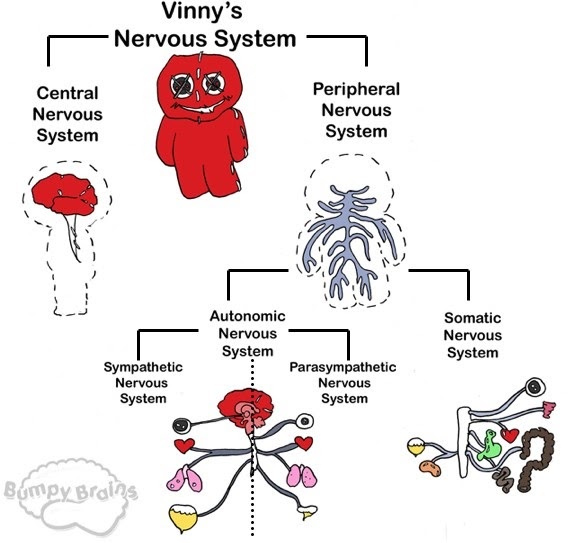
The nervous system comprises the somatic (voluntary) nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. The somatic nervous system is the side of the system that deals with commands that we are aware of and can control e.g. the connection between the brain, spinal cord and skeletal muscles. The autonomic nervous system is the side that governs involuntary and reflex functions such as blood vessel dilation and heart rate.
The spinal cord


