DNA structure
What are the strands made of?
DNA replication
The genetic code
mRNA
mRNA / DNA
tRNA (Transfer RNA)
Protein synthesis
Transcription
Splicing
Translation
Cause of Mutations
The Effects of Mutations
DNA is a double helix i.e. two individual strands running along each other in an anti-parallel way, connected to one another by relatively weak hydrogen bonds. DNA’s structure can be learned easily by thinking about the strands and the “stuff in-between” separately.
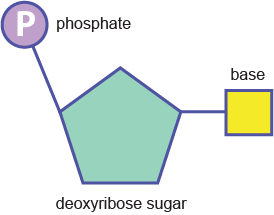
Phosphodiester bonds between nucleotides (above) create the backbone:
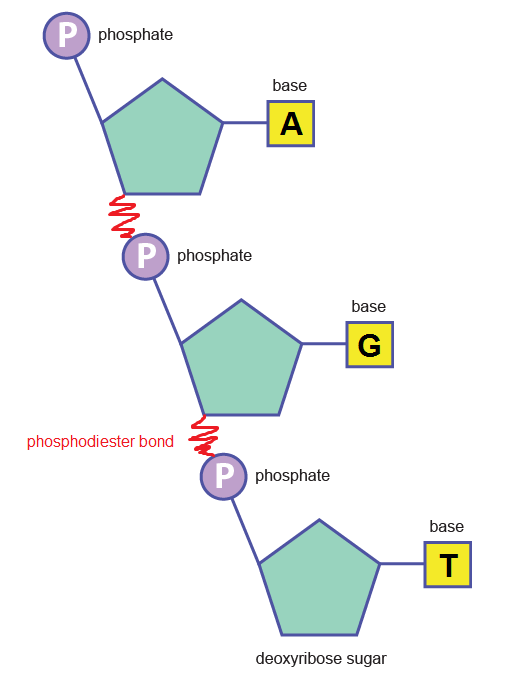
What is the centre made of?
Attached to the sugar molecules in the backbone are a different type of molecule called nitrogenous base. There are 4 bases in DNA: adenine, thymine, cytosine and guanine. These are abbreviated by their initials: A, T, C and G….

