Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Carbohydrates
Starch is hydrolysed to disaccharides and trisaccharides before further reactions by other enzymes convert the products into glucose, the ultimate usable nutrient.
The hydrolysis of starch is catalysed by amylase. As this step of carbohydrate digestion begins in the mouth, initially non-sweet carbs like potatoes or rice gradually sweeten in taste before being swallowed for their digestion to continue.
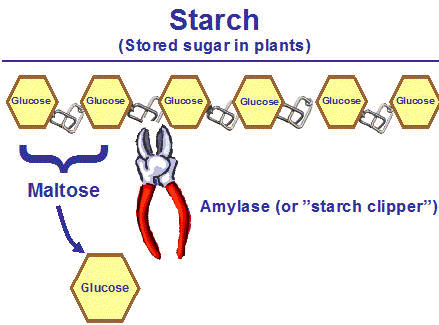
Amylase thus breaks the glycosidic bonds between glucose monomers. It doesn’t do so for each and every one of them, so the resulting disaccharide for example would be maltose (glucose-glucose).
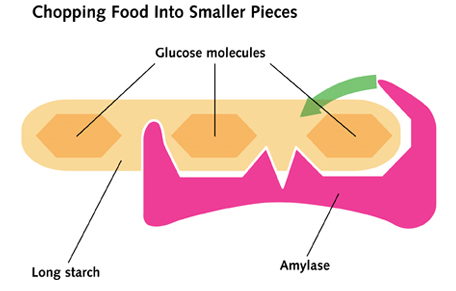
At this stage, whether in the mouth or stomach, disaccharides or trisaccharides have yet to be hydrolysed further into glucose or their constituent monomer. This takes place just before absorption in the small intestine (ileum) and is catalysed by membrane-bound…
