The Chordata phylum covers mammals and birds, and is distinguished by the spinal cord that gives the body its structural support alongside a jointed system of calcified bones.

Chordata species are both bilaterally symmetrical and segmented, and the gut similarly includes both a mouth and an anus, with specialised digestion regions.
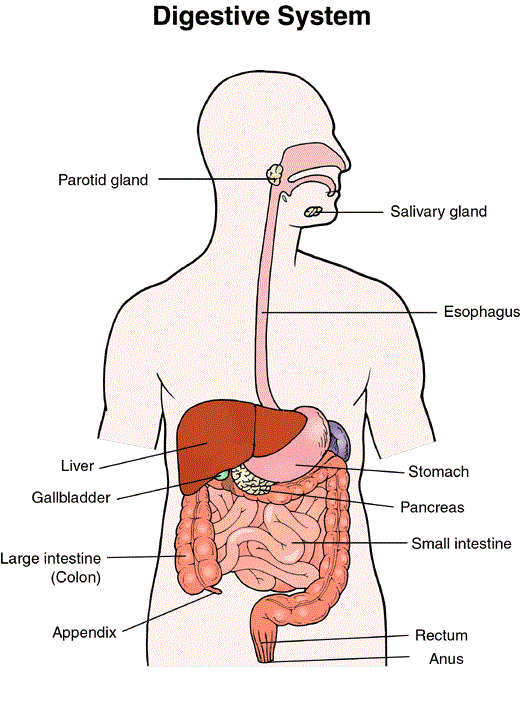
Saliva and mastication (chewing) prepare ingested food into a bolus which passes down the esophagus upon swallowing, into the stomach. The presence of enzymes, churning and acidic pH contributes to the further breaking down of food. Different food molecules require different processes for digestion.
In this sense, Chordata are similar to Arthropoda and Annelida, while being different to…
