Measuring metabolic rate
Adaptations in organisms with different metabolic rates
Living under low oxygen
Maximum oxygen uptake and fitness in humans
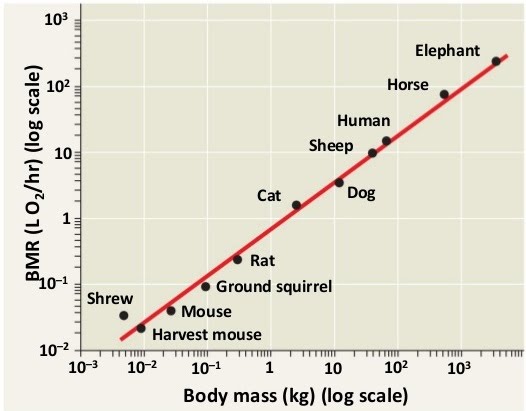
Measuring metabolic rate
The sum of all metabolic reactions in the body can be measured as a function of oxygen consumption, carbon dioxide production and heat production. Oxygen is needed in aerobic respiration, carbon dioxide is a byproduct of respiration, while heat is lost energy by many reactions.
The higher these variables, the higher the metabolic rate is. Due to the big range of metabolic rates between organisms at rest versus active, for comparison purposes the resting metabolic rate is obtained.