☠️ Threats to biodiversity
Low populations in exploited species
Habitat loss impacts species richness
Introduced species disrupt indigenous species
Climate change
Low populations in exploited species
As populations of certain species become smaller, for example due to overfishing, their genetic diversity shrinks, and inbreeding predisposes them to deleterious phenotypes. There is a threshold for how low a population can get before it can no longer be saved from extinction. This differs between species, and there are species which are inherently of low genetic diversity without having problems.
Recovery of populations following exploitation involves letting them breed without interference to their previous, high level of individuals, and thus refresh their genetic diversity.
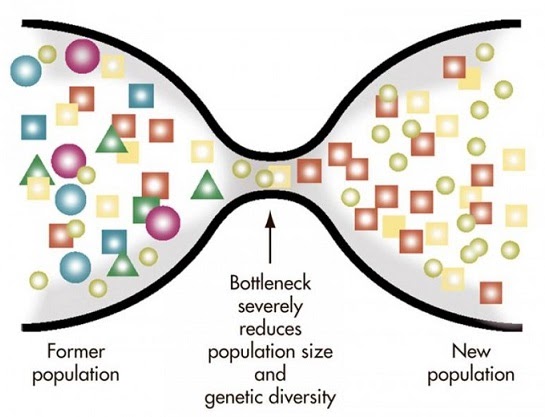
Genetic bottlenecks
The only difference between the founder effect and genetic bottlenecks is the way in which the new genetic pool is formed. In the founder effect the new pool is formed when a few individuals from a population become geographically isolated, while in genetic bottlenecks the new gene pool is formed when only a few individuals from a population survive a mass disaster, or are the only ones to breed.
The effect is the same: the genetic variation of the new population is decreased compared to the original population.
Habitat loss impacts species richness
Different species occupy different niches in a habitat. As such, there are edge species that thrive at the boundary between habitats, and interior species that reside in the heart of the habitat. Damage to habitats at their edges can create habitat fragmentation..

