????️ Circulation
The circulatory system
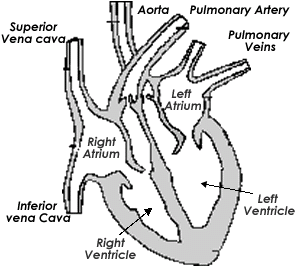
Heart
Blood vessels
Function
Structure
Control of heart rate
Interpreting heart function data
Blood
Components
Coagulation (clotting)
Atherosclerosis
Atheroma
Diet
Smoking
The advantages of double circulation in mammals as opposed to single circulation (such as in bony fish) include the option to have a higher blood pressure and splitting oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. As blood gets oxygenated in the lungs, the diffusion process takes time, which has the blood at lower pressure. On the other hand, the already oxygenated blood can be pumped around the body at higher pressure, allowing for bigger organisms and increased metabolic activity. Splitting deoxygenated blood from oxygenated blood is key to this.
The atrioventricular valves and semilunar valves play an important role in ensuring proper heart function. The former ensure no blood flows back into the atria from the ventricles, while the latter ensure no blood flows from the ventricles into the atria.
Electrical impulses cause heart muscle contraction which creates an increased pressure of blood, resulting in it being pushed in a certain direction, with the valves opening in its way. The sequence of events in heart contraction is this:
Both atria contract – atrial systole
Both ventricles contract – ventricular systole
All chambers relax – diastole
The heart muscle contracts without brain stimulation – the brain only controls the speed. Electrical impulses start in the..