Mutations
What are mutations?
Types of mutations
Mutations and cancer
Polyploidy and Evolutions
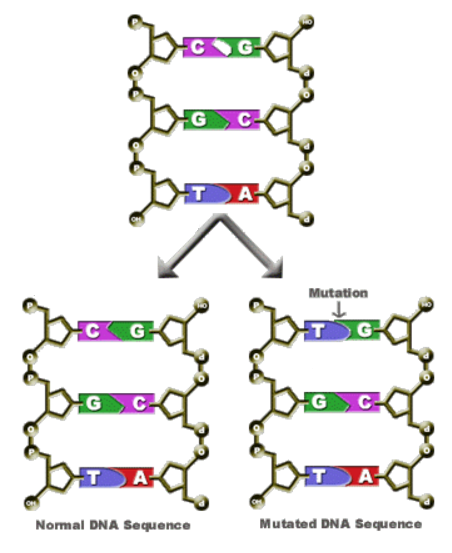
Mutations are a random occurrence during DNA replication and the rate of mutation is influenced by external factors such as UV radiation. Mutation occurs spontaneously.
There are many different types of mutation:
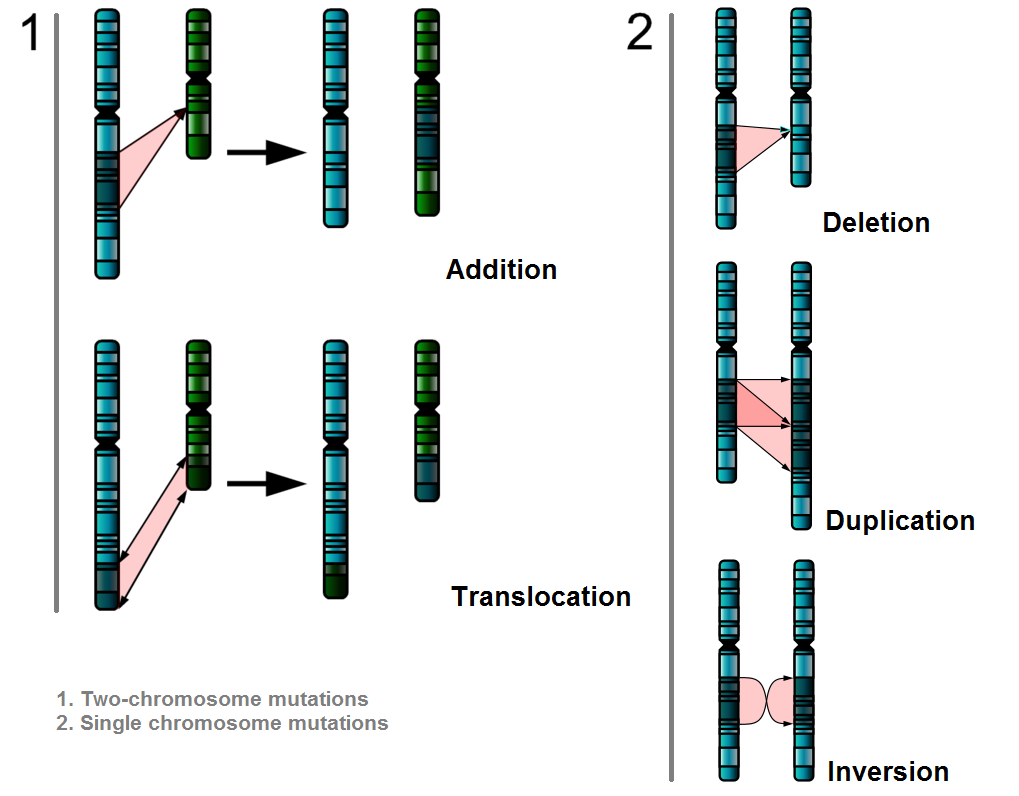
1. Deletion where one or more nucleotide bases are deleted. AGTCA becomes AGCA
2. Substitution where one or more nucleotide bases are replaced by others. AGTCA becomes AGTCG
3. Addition where one or more nucleotide bases are added as extra. AGTCA becomes ATGTCA
4. Inversion where a section of DNA is inverted e.g. AGTTCATTCCAGG becomes AGTTCCCTTAAGG
5. Duplication where one or more nucleotide bases are repeated e.g. AAGTCG becomes AAGTCGAAGTCG
6. Translocation where one or more nucleotide bases are moved between non-homologous chromosomes e.g. AAGCTT on human chromosome 1 is moved and becomes AAGCTT on human chromosome 3.
Since the genetic code is degenerate, it’s possible that a mutation won’t have any effect whatsoever! This represents silent mutations. If 2 different triplet codes translate into the same amino acid, the polypeptide chain will remain unchanged. This of course only applies to…..


