Food supply, plant growth and productivity
Food supply
Photosynthesis
Food supply
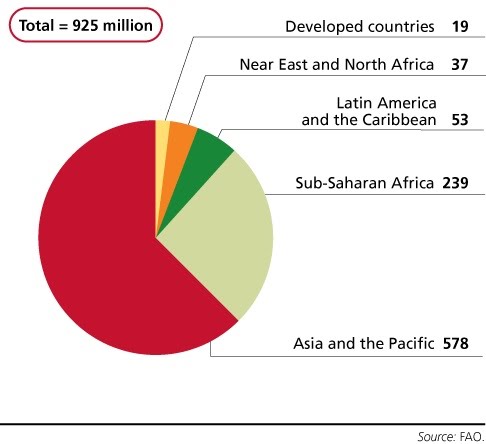
Increasing human population leads to concerns over food security. Food security refers to people’s ability to access food of a sufficient quality and quantity.
Food production must increase, but do so in a sustainable way that doesn’t compromise the natural resources it ultimately depends on.
The “pillars” of food security are availability, access, utilisation and stability.
Availability refers to the production, distribution and exchange of food, and includes issues of land ownership, crop selection, livestock management and harvesting.
Access refers to affordability, food preferences and food allocation. Access may be challenged by fluctuations in food prices, with those in poverty being affected the most. Those who can afford higher prices would not suffer from unexpected spikes.
Utilisation is how the metabolism of humans makes the most of the food that is available. Infection can lead to some food being used by intestinal parasites instead, while sanitation determines how much food can be eaten safely. The cultural settings of food consumption can also affect utilisation, while health can determine how well food is metabolised.
Finally, stability refers to the ability to maintain food security over time. Transient shortages caused by droughts or conflicts impact stability, and can make households more susceptible to chronic instability if transient famine occurs repeatedly.
Food production relies on plant growth and photosynthesis, as applied to many plant crops including cereals, potato, roots and legumes. Photosynthesis relies on optimal temperature, CO2 concentration and light.
If photosynthesis had no limiting factors, what would glasshouse growers have to exploit?

Precisely. Photosynthesis, just like all other physiological processes in living things as well as chemicals and beyond, is subject to external influences. The main factors that weigh in on the efficiency and speed of photosynthesis are :
Temperature
CO2 Concentration
Light intensity
Both the concentration of carbon dioxide and the intensity of light are similar in that they are both direct ingredients in the overall photosynthesis reaction. But since temperature insists on having the first say….


