Gene Mutation
The Cause of Mutations
The Effect of Mutations
Mutations and Cancer
The Cause of Mutations
Mutations are a random occurrence during DNA replication and the rate of mutation is influenced by external factors such as UV radiation. There are different types of mutation:
Deletion where a nucleotide base is deleted. AGTCA becomes AGCA.
Substitution where a nucleotide base is replaced by another. AGTCA becomes AGTCG.
Insertion where a nucleotide base is added as extra. AGTCA becomes ATGTCA.
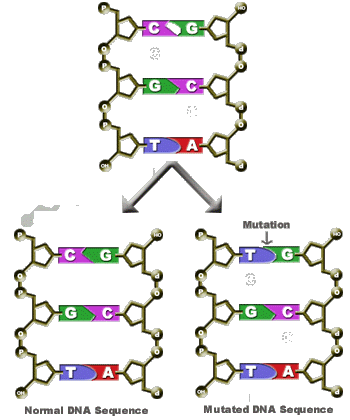
The Effect of Mutations
Since the genetic code is degenerate, it’s possible that a mutation won’t have any effect whatsoever! This represents silent mutations. If 2 different triplet codes translate into the same amino acid, the polypeptide chain will remain unchanged. This of course only applies to applies to substitutions.
Another scenario where a mutation may cause no effect is if it arises in an intron. Since these are removed before mRNA is translated, no mutations would be carried along.
What happens if a base is deleted or added?
