Nervous transmission
Introduction
Action potential
The Myelin Sheath
Synapse
Introduction
Let’s delve into the basics of nervous transmission by looking at a motor neurone. Here is the structure of a myelinated motor neurone:
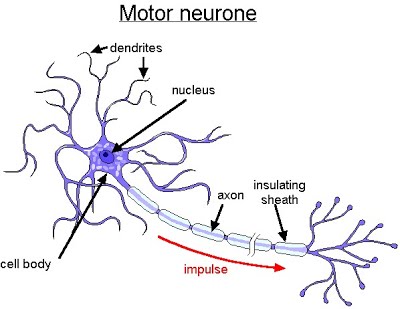
Labelled “insulating sheath”, the myelin sheath is responsible for protecting the electrical impulses that run across the neurone.
But first, what happens in a resting state where no impulses are being sent?
This is the resting potential where the membrane permeability differentiates between sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+) ions so that at any given time there are more Na+ ions outside than inside and more K+ ions inside than outside.
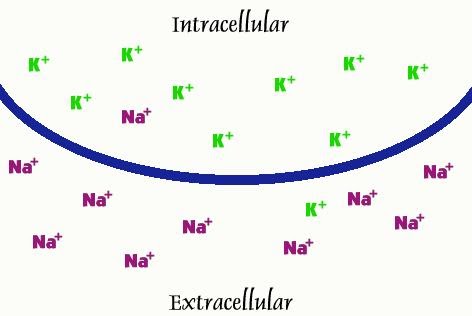
According to these electrochemical gradients, Na+ ions should move back inside to balance out their concentration (equilibrate) while K+ ions should move back outside the membrane until the..


