Principles (Coordination)
Electrically
Chemically
Histamine
Prostaglandins
Tropism
Introduction
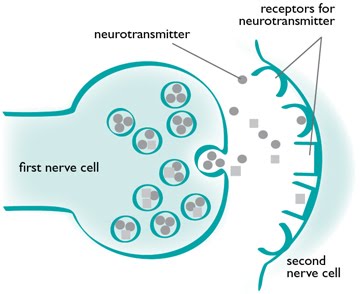
Effectors in the body such as muscles and glands may get their signals to contract or secrete substances in two ways: electrically by nerve impulses or chemically by hormones.
Nerve cells have electrical impulses pass along them which results in their secretion of a neurotransmitter onto the target cells which respond quickly, locally and in a short-lived way.
Hormones on the other hand circulate in the bloodstream, reaching distant target cells and exerting a long-lasting but slow effect.