Introduction
Broad bean
Germination
Maize
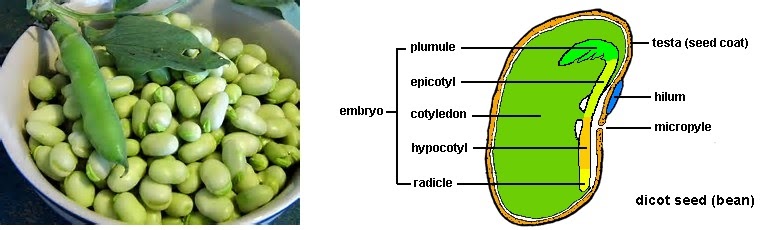
In this case, the whole pod is the “fruit” while the bean is the seed. The testa is the outer coat that protects the embryo against dehydration and infection by outside agents.
The hilum is the scar left on the seed following its detachment from the wall of the ovary.
Germination
The micropyle was initially the opening through which the pollen entered the ovule for pollination, and now can serve to direct the emerging seedling out into the ground during germination. This can happen after a period of dormancy during which the seedling does not develop. This can help the plant save energy, and only develop in good conditions. Hydration of the seed can kickstart germination…
