What is tuberculosis?
How is TB passed?
Treatments
Vaccine
What is tuberculosis?
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease of the lungs which causes constant coughing with blood, shortness of breath, fever and weight loss over the years. Every year 2 million people die from TB out of 8-10 million who get the disease. Far more people, around 2 billion, carry the TB bacteria on them without having the disease.
How is TB transmitted?
TB is passed on between people by inhaling droplets from the air infected with the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis. When the infection is confirmed, patients are isolated for up to 4 weeks and put on a course of antibiotics for up to 6 months.
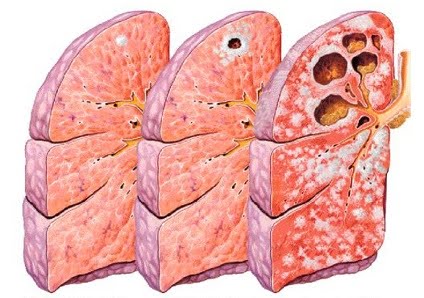
When bacteria reach the alveoli, the immune system reacts by surrounding them with white blood cells, which results in the formation of scar tissue. The shortness of breath symptom is caused by less oxygen reaching the circulatory system due to a decreased surface area for diffusion in the lungs, as many alveoli are damaged.
Treatment
Treatment involves a course of antibiotics which can be lengthy, resulting in many patients stopping at the first signs of amelioration of their symptoms. This causes resistance in the bacteria, which come back to cause disease. Moreover, antibiotic-resistant strains have emerged. There are multi-drug resistant strains which are not affected by the main antibiotics (isoniazid and rifampicin), and even totally drug resistant…
