Communicable disease
Bacterial identification
Incidence and prevalence of disease
Control and prevention
Communicable disease
Communicable disease spreads from affected individuals to those unaffected. Pathogens are microorganisms which can cause disease. These include bacteria, viruses and fungi. Have a look at the little things!
Pathogens can cause disease when they invade the interface between an organism and their environment. This could be someone’s skin, lungs, digestive system, etc.
There are multiple ways in which pathogens cause disease. Bacteria can produce toxins, viruses take over cellular machinery such as enzymes and nutrients and destroy the cells in the process, while fungi can secrete enzymes that break down host tissue.
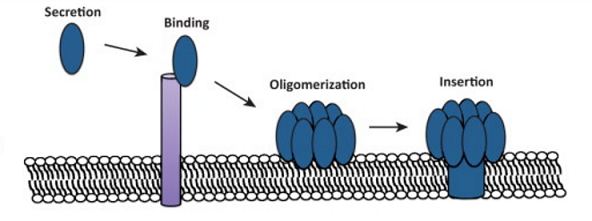
There are many different kinds of bacterial toxin e.g. by Staph. aureus, such as protein barrels that integrate into the plasma membrane of host cells and cause their contents to leak out through these huge pores created by the barrel shape.
Viruses are tiny microscopic entities that have absolutely no activity whatsoever. In the presence of a larger organism of their specific fit (and there are viruses to target anything), they come alive by hijacking its life tools: nutrients, energy, ribosomes, you name it.
They only carry the genetic information they need to invade and replicate. Invade and replicate. A bit of a glitch of life, or the perfect expression of it?….
