Introduction
Transcription: DNA to mRNA
Splicing: pre-mRNA to mRNA
Translation: mRNA to tRNA
Result: protein synthesis
Introducion
Proteins are made up of amino acids linked by peptide bonds, therefore a protein may be referred to as a polypeptide (of course, some proteins such as haemoglobin have extra bits to them). All are encoded for by the information stored in DNA. Let’s see how exactly this happens.
Transcription: DNA to mRNA
In a process called transcription, mRNA is formed based on DNA. The bases on the coding strand of DNA are transcribed into a new molecule, mRNA, which is synthesised by the enzyme RNA polymerase.
Wanna see more detail?
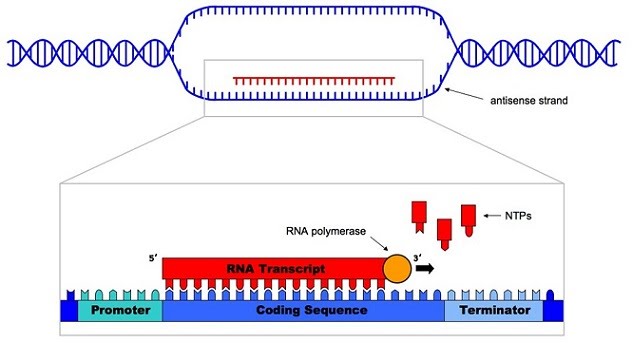
As you can see, the DNA double helix unwinds, RNA polymerase anneals to the coding strand and recruits freely available bases (A, U, C, G) to build an mRNA strand.
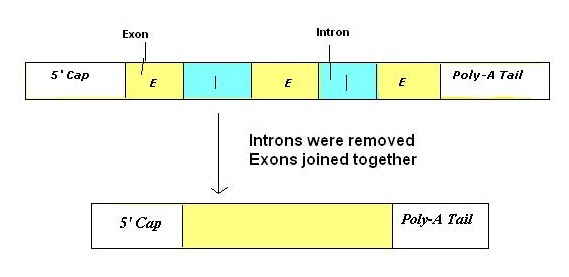
Splicing: pre-mRNA to mRNA
In eukaryotes, genes contain non-coding sequences which must be removed before mRNA is used to produce proteins. These are called introns as opposed to exons which are coding sequences. Splicing therefore is the process of excising (cutting out) introns to be left with mRNA containing purely coding sequence.