Sex linkage refers to a trait that is carried on a sex chromosome like the X chromosome. Because someone might have a different number or combination of sex chromosomes such as a single X chromosome or two X chromosomes, the expression of various traits can differ.
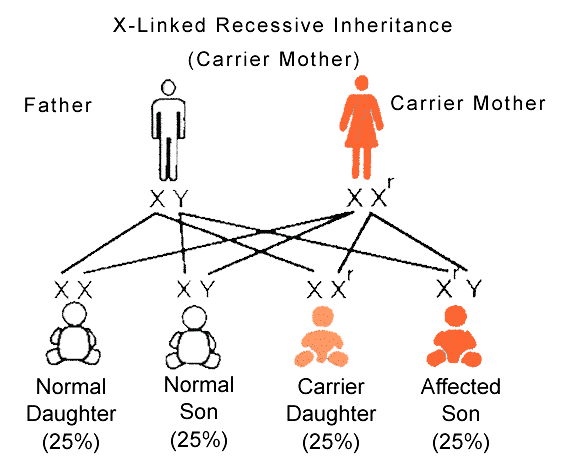
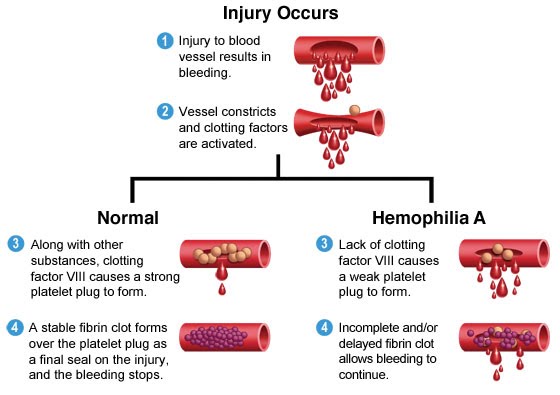
If for example the allele on the affected X chromosome means that an essential protein isn’t being made, the carrier XX child has another unaffected X chromosome to fall back on and be able to produce the essential protein. The carrier XY child only has the affected X chromosome and cannot make the protein. This results in an illness for example, such as haemophilia. Haemophilia is a blood clotting disorder in which excessive bleeding takes place because the platelet plug and fibrin which are supposed to stop bleeding do not work fully.
Another example of an X-linked condition is Duchenne muscular dystrophy which affects around 1 in every few thousand children with an XY genotype. It is a progressive muscle degeneration condition that affects mobility, and in the long term requires…
