Unicellular nutrition
Multicellular nutrition
Unicellular nutrition
Single cells such as Amoeba absorb food particles from their environment and digest them directly inside themselves (their single cell).
There is no designated area of the cell where phagocytosis takes place as the food gets absorbed. Pseudopods can extend out of the cell to aid with capturing the food.
During absorption, vesicles within the plasma membrane of Amoeba can be formed to imbibe the food particles.
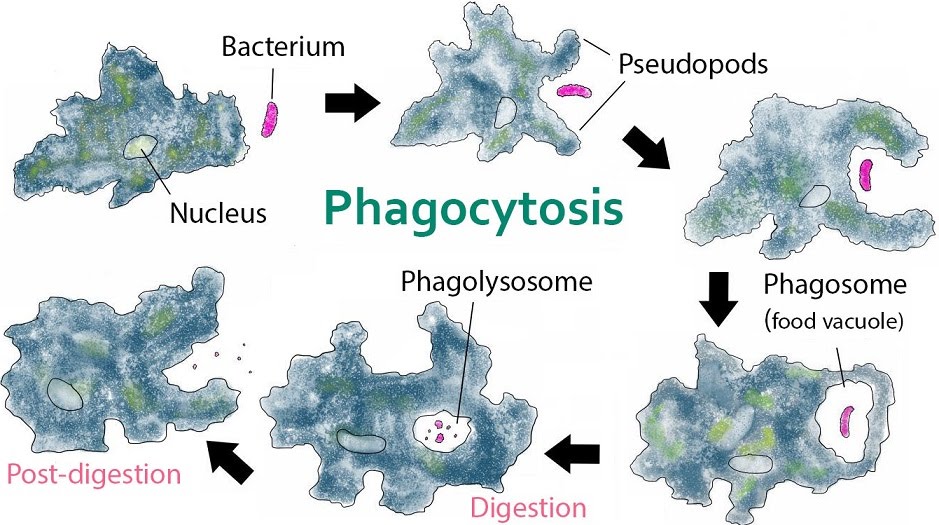
Digestive enzymes inside the phagolysosome break down the food into smaller particles, and excretory byproducts are released back into the environment.
Multicellular nutrition
Once an organism is multicellular, it can concoct actual structures dedicated to digestion. The most basic such structures involve simple, undifferentiated sac-like guts with just a single opening, while more complex ones are tubes with two openings (one for ingestion and one for egestion; so the nutrients in food and the waste products don’t mix together) and separate regions for digesting different types of food substance…
