What is involved in gene therapy?
Associated problems
Other issues
Current conditions treated with gene therapy
What is involved in gene therapy?
Gene therapy involves inserting a functional gene into a patient who lacks it, or needs supplementary support. This works for conditions which are caused by a single faulty gene rather than multiple genes. Once the new DNA is taken up in the cell nucleus, the gene is expressed like any other gene.
The vector used to deliver the gene is a harmlessvirus.
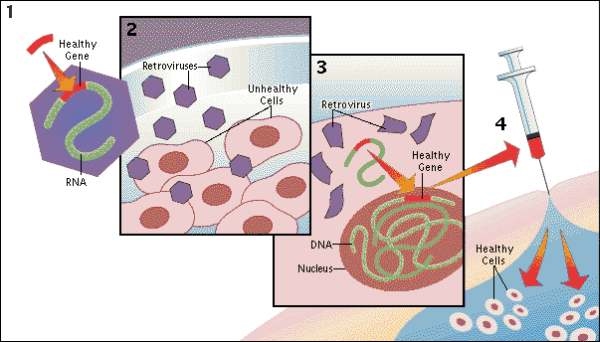
One problem associated with gene therapy is the immune reaction the body has to the virus. This may cause inflammation and other potentially serious side effects. Another issue is that of maintaining the effects of the healthy gene inserted into target cells. If these are recycled quickly or don’t pass on the new gene to their offspring cells, then the therapeutic effect stops there, and the case is that multiple rounds of gene therapy must be administered.
Conditions currently treated with gene therapy include: cystic fibrosis, haemophilia, Parkinson’s disease, muscular dystrophy, sickle cell anaemia among many others. One particular…
